Defense of Little Round Top

James R. Brann

Late in the afternoon of July 2, 1863, on a boulder-strewn hillside in southern Pennsylvania, Union Colonel Joshua Lawrence Chamberlain dashed headlong into history, leading his 20th Maine Regiment in perhaps the most famous counterattack of the Civil War. The regiment’s sudden, desperate bayonet charge blunted the Confederate assault on Little Round Top and has been credited with saving Major General George Gordon Meade’s Army of the Potomac, winning the Battle of Gettysburg and setting the South on a long, irreversible path to defeat.
For many years, historians and writers have given the lion’s share of the credit for the 20th’s dramatic action on Little Round Top to Chamberlain. Numerous books and even the popular movie Gettysburg have helped fuel adulation for the Union officer. But did Chamberlain really deserve the credit he received? Or, to put it another way, did he deserve all the credit? Answering that question adequately requires taking another look at the Battle of Gettysburg and the hell-raising fighting that occurred among the scattered stones of Little Round Top.
On June 3, 1863, Confederate General Robert E. Lee began the Army of Northern Virginia’s second invasion of the North. Lee’s main objective was to move across the Potomac River and try to separate the Union forces from Washington. When the Army of the Potomac’s commander, Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker, belatedly became aware of the Confederates’ movement, he began to force-march his army north, trying to keep Lee to the west and screen Washington from the Rebel troops. On June 28, as the bulk of the Federal troops enjoyed a brief respite near Frederick, Md., Meade replaced Hooker as commander of the Army of the Potomac.

Meade faced a daunting task. By June 30 Lee’s forces, including those of corps commanders Lt. Gens. James ‘Pete Longstreet and Ambrose P. Hill, were marching on the Chambersburg Road in southern Pennsylvania, while Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell was leading his corps westward from York. Major General J.E.B. Stuart, directing Lee’s cavalry, had not returned to the main Southern column from his screening mission around the Union forces. In fact, Stuart would not return until July 2, a crucial error in judgment.
Lacking adequate intelligence from his scouting forces, Lee directed his army to gather at Gettysburg. The general did not want to fight at Gettysburg, but alert Union horsemen had reached the area — a fact that would put a wrinkle in Lee’s plans. When Confederate Brig. Gen. James J. Pettigrew approached the town leading a 2,584-man brigade that was part of Maj. Gen. Henry Heth’s division, he became aware of the Union cavalry force positioned there. Pettigrew withdrew his troops and then reported back to Heth. The next day, July 1, Heth headed toward Gettysburg with four brigades of infantry to drive off the reported Union troopers and secure the town.
To Heth’s surprise, waiting for him was Union Brig. Gen. John Buford, who had dismounted and deployed his cavalry on McPherson’s Ridge, west of Gettysburg. Buford’s forces fired first, temporarily halting Heth’s force and starting the Battle of Gettysburg. Both sides sent dispatches to inform their superiors of the confrontation. Meade reinforced his Union position with the I Corps, which was now led by Maj. Gen. Abner Doubleday since Maj. Gen. John Reynolds had been mortally wounded earlier that day. Additional Union reinforcements came from Maj. Gens. Henry W. Slocum’s XII Corps and Daniel Sickles’ III Corps. Throughout the morning, Confederate pressure continued to build against the Union line.
Although spread thinly, the Union troopers held their ground with repeating carbines. As the fighting intensified, both sides added more infantry divisions to the battle. The Confederates managed to exploit weaknesses in the Federals’ deployment, and their attacks caused heavy losses to the Union troops, who were forced to retreat. Confederate General Ewell’s failure to carry out his orders and attack Cemetery Hill on the afternoon of July 1 wasted a golden opportunity for a quick, decisive victory. The Union had lost 4,000 men by that time — and the town of Gettysburg itself — but Meade quickly moved reinforcing divisions onto the high ground south of Gettysburg. The two armies spent a restless night.
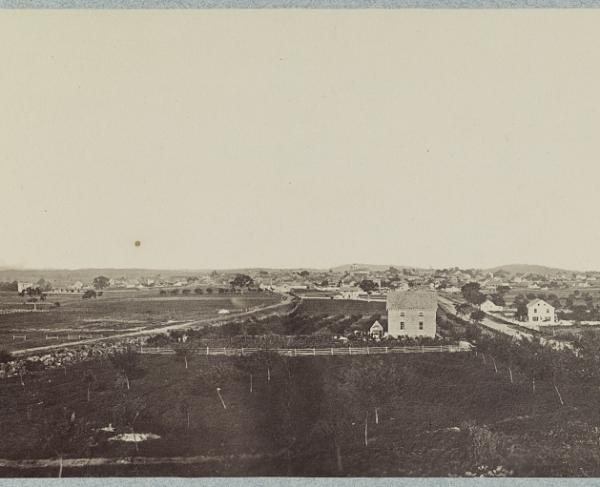
The Union defensive line on aptly named Cemetery Ridge resembled an inverted fishhook, extending from Culp’s Hill on the north, down Cemetery Ridge and southward toward Big and Little Round Tops. Although the 650-foot-high Little Round Top was overshadowed by its larger neighbor, its position was more important because much of the hill was cleared of trees and it could better accommodate troops. Strategically, Little Round Top held the key to the developing battle. If the Southern troops could take and hold the hill, they could theoretically roll up the entire Union line.
On the morning of July 2, Little Round Top proper held perhaps just a handful of Federal soldiers. Pennsylvania native Brig. Gen. John W. Geary’s division was aligned just north of the hill and was the largest Union force in the immediate area. Geary was ordered to rejoin the rest of his XII Corps at Culp’s Hill after elements of Sickles’ III Corps took his place. In the confusion of shifting troops, however, Geary pulled his men out too soon, before Sickles’ men had moved to replace them. Little Round Top was left uncovered. Later, when Sickles’ infantry did arrive, the controversial general moved his men, without orders, westward toward the Emmitsburg Road. Once again Little Round Top went wanting for protectors in blue.

Robert E. Lee, with his eerie sense of a battlefield, was hastily assembling a force to attack the Union left, but it would take him the greater part of the day to get his men ready to strike. Meanwhile, Meade also sensed something significant about the two adjacent hills to his left. That afternoon he sent his chief of engineers, Brig. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren, to assess the situation. To his utter chagrin, Warren found Little Round Top completely undefended. He hastily sent messengers to Meade and Sickles, requesting immediate assistance. Sickles, by that time hotly engaged with elements of Longstreet’s corps, had none to spare. But Colonel Strong Vincent, who commanded the 3rd Brigade of Brig. Gen. Charles Griffin’s 1st Division of the V Corps, received word from a harried courier about the threat to Little Round Top and led his men to the hill at the double-quick. Vincent’s brigade included the 44th New York, 16th Michigan, 83rd Pennsylvania and the 358-man 20th Maine under Joshua L. Chamberlain.
The 34-year-old Chamberlain was one of the most interesting figures in the Civil War. A highly cultured, somewhat sedentary professor of modern languages at Maine’s exclusive Bowdoin College, he had sat out the first year of the war on Bowdoin’s stately campus. But in July 1862, sensing perhaps that the war was going to last a good deal longer than he had first believed, Chamberlain offered his services to the Union cause. I have always been interested in military matters, he informed Maine Governor Israel Washburn, and what I do not know in that line, I know how to learn. He was given command of the newly formed 20th Maine, a unit comprised of extra men left over from other new regiments. It was not, Chamberlain noted, one of the state’s favorite fighting units — No county claimed it; no city gave it a flag; and there was no send-off at the station.

The 20th Maine had been organized under President Abraham Lincoln’s second call for troops on July 2, 1862. The regiment initially fielded a total complement of 1,621 men, but by the time of the Battle of Gettysburg the stress of campaigning had reduced the regiment’s ranks to some 266 soldiers, and the 20th was considered a weak link in Vincent’s brigade. Fortune, however, was to smile on Chamberlain’s regiment in the form of unexpected reinforcements.
On May 23, 1863, 120 three-year enlistees from the 2nd Maine Infantry were marched under guard into the regimental area of the 20th Maine. The 2nd Maine men were in a state of mutiny and refused to fight, angry because the bulk of the regiment — men with only two-year enlistments — had been discharged and sent home, and the regiment had been disbanded. The mutineers claimed they had only enlisted to fight under the 2nd Maine flag, and if their flag went home, so should they. By law, however, the men still owed the Army another year of service.
Chamberlain had orders to shoot the mutineers if they refused duty. Fortunately for the men of the 2nd Maine, Chamberlain was born and grew up in Brewer, the twin city to Bangor across the Penobscot River where the 2nd Maine regiment was recruited. The mutineers were not just soldiers but also Chamberlain’s childhood neighbors. Instead of shooting them, Chamberlain wisely distributed the 2nd Maine veterans evenly to fill out the 20th Maine’s ranks and integrate experienced soldiers among the untested 20th Maine. He sympathized with the mutineers and wrote to Maine Governor Abner Coburn, asking that he write to the men personally about the mix-up in three-year versus two-year contracts they had signed. On Little Round Top the 120 experienced combat veterans from the 2nd Maine brought the 20th’s ranks up to 386 infantrymen and helped hold Chamberlain’s wobbling line together.
As he arrived on Little Round Top, Colonel Vincent chose a line of defense that started on the west slope of the hill. When the first regiments reached the rocky outcrops in that area, Vincent put them into line. The 16th Michigan took up a position on the right flank, and the 44th New York and 83rd Pennsylvania held the center. Later in life, Chamberlain wrote that his regiment was the first in line, but it actually took up its position last, curving its line back around to the east and forming the Union Army’s extreme left flank.
The last thing Vincent told Chamberlain was: This is the left of the Union line. You are to hold this ground at all costs! Chamberlain ordered the regiment to go on line by file. He deployed Company B, recruited from Piscataquis County and commanded by level-headed Captain Walter G. Morrill of Williamsburg, forward to the regiment’s left front flank as skirmishers. Company B, with its 44 men, was subsequently cut off by a flanking attack by the enemy, leaving the 20th with only 314 armed men on the main regimental line.
Also helping to defend Little Round Top were Major Homer R. Stoughton’s 2nd U.S. Sharpshooters, armed with .52-caliber breechloading rifles. These sharpshooters’ skirmishing abilities were unequaled in the Union Army, and a 14-man squad was attached to Company B. The men took up a position in a ravine east of Little Round Top.
Shortly after the Federals had taken up their positions, the 824 men of the 4th and 5th Texas regiments of Maj. Gen. John B. Hood’s division hammered up the slope of Little Round Top, pushing toward the center and right of Vincent’s line. During that assault, Captain James H. Nichols, the commander of the 20th Maine’s Company K, ran to alert Chamberlain that the Confederates seemed to be extending their line toward the regiment’s left. Chamberlain called his company commanders together and told them his battle plans. With the new information from Nichols, Chamberlain ordered a right-angle formation, extending his line farther to the east.
Meanwhile, Colonel Vincent tried to rally his 3rd Brigade as the 16th Michigan staggered under the heavy assault by the 4th and 5th Texas. Just when the Federals were on the verge of collapse, Colonel Patrick O’Rorke led the 140th New York Zouaves into the gap to save Vincent’s brigade. Both Vincent and O’Rorke paid with their lives for their heroism.
Elements of Hood’s division, the 15th and 47th Alabama, then began to smash into the Maine troops. Hood ordered these regiments, led by Colonel William C. Oates, to find the Union left, turn it and capture Round Top.

Twenty-five-year-old Color Sgt. Andrew J. Tozier of the 2nd Maine quickly emerged as an unlikely hero, and he was later awarded the Medal of Honor for his bravery. It had been Chamberlain’s idea to elevate Tozier to the post of color sergeant for the 20th Maine, a move designed to instill a new esprit de corps in the mutineers. Color sergeant was a dangerous but coveted position in Civil War regiments, generally manned by the bravest soldier in the unit. As the 20th Maine’s center began to break and give ground in the face of the Alabama regiments’ onslaught, Tozier stood firm, remaining upright as Southern bullets buzzed and snapped in the air around him. Tozier’s personal gallantry in defending the 20th Maine’s colors became the regimental rallying point for Companies D, E and F to retake the center. Were it not for Tozier’s heroic stand, the 20th Maine would likely have been beaten at that decisive point in the battle.
When their ammunition had almost run out, Chamberlain decided to fix bayonets and charge down into the two Alabama regiments. Chamberlain later said he communicated his decision to counterattack to Captain Ellis Spear, the acting battalion commander of the unit’s left flank. Spear, however, claimed he received no such orders.
Corporal Elisha Coan, a member of the 20th Maine’s color guard, claimed that 1st Lt. Holman S. Melcher, the acting commander of Company F, actually conceived the idea to advance the colors and that Colonel Chamberlain initially hesitated, fearing that it would be extremely hazardous. Coan said other officers joined Melcher in urging a forward movement.
Chamberlain — whose right foot had been pieced by a shell fragment or a stone chip — then limped along the regimental line giving instructions to align the left side of the regiment with the right. After Chamberlain returned to the regimental center, Melcher asked permission to retrieve his wounded from the front. Chamberlain replied, Yes, I am about to order a right wheel forward of the whole regiment. (Chamberlain himself claimed later to have said, yes, sir, in a moment! I am about to order a charge.)
Chamberlain ordered a right-wheel maneuver and took up a place behind Tozier. There is some disagreement about exactly what Chamberlain said to order the bayonet charge. One story is that he screamed: Bayonet! Forward to the right! Chamberlain claimed later that one word — Bayonet! — was enough and that it was vain to order Forward because no one could hear it over the noise. Nor was there time. Right wheel or Bayonet! Forward to the right was perhaps someone’s post-war idea of what Chamberlain would have said if time permitted. The state-appointed Maine commission that later gathered facts regarding Maine’s contribution to the Battle of Gettysburg maintained that Melcher sprang forward as Chamberlain yelled, Bayonet! and that Chamberlain himself was abreast of the colors.
With all the confusion and noise on Little Round Top that day, if anything other than bayonet had been said it probably would not have mattered, anyway. An infantryman who is out of ammunition, faced with being cut down on the next enemy charge, and hearing the metal-to-metal sound of bayonets being put on en masse knows the intent of the upcoming order without actually hearing it. In all likelihood Lieutenant Melcher conceived the idea to advance the colors to retrieve the wounded, but Chamberlain expanded upon the idea, deciding to have the whole regiment conduct a bayonet attack. In doing so, Chamberlain exercised effective battle command.

After Chamberlain ordered Bayonet, the Union line hesitated until Melcher sprang out in front of the line with his sword flashing. Captain Spear said he never received a formal order to charge — he charged only after he saw the colors start forward.
The Rev. Theodore Gerrish, then a private in Company H, stated that Melcher led the men down the slope when the enemy was only 30 yards away. Corporal Coan said the men hesitated when Melcher ordered them forward because they were not sure if the colonel had sanctioned the attack. Chamberlain claimed there was no hesitation and said that the line quivered for the start. Captain Nichols wrote in 1882 that Company K never hesitated. Perhaps Company H did hesitate on the left because they were taking heavy fire when the charge started. Company K probably did not delay since the right side of the regiment was not experiencing heavy fire at the time. Most evidence indicates that Chamberlain ordered the charge, and Melcher was the first officer down the slopes. Melcher was an inspiration to the tiring regiment as he sprang a full 10 paces to the front with his sword glittering in the sunlight.
Another crisis soon faced the Maine soldiers when the left side of the regiment drew even with the right, short of its planned position. Melcher broke this momentary disruption by running down the slope screaming: Come on! Come on boys! with Tozier beside him and Chamberlain not far behind.
Great responsibility also fell upon Captain Spear, whose flank was to start the attack — otherwise the charge would not pivot and work to its fullest potential. But Spear gets curiously little credit for marshaling and organizing the tactics of the left flank of the 20th. Spear literally controlled half the regiment during the climactic counterattack. The lack of credit perhaps helped create the rift that later developed between him and Chamberlain.
During the charge, a second enemy line of the 15th and 47th Alabama tried to make a stand near a stone wall. For a moment it looked as though the Confederates might succeed in halting the Unionists and breaking their momentum. But, using the classic element of surprise, Captain Morrill’s Company B rose up from behind a stone wall and fired a volley into the Confederates’ rear, breaking the will of the enemy troops. Confederate reports showed that the Union company had been magnified into two regiments. According to Confederate Colonel Oates, it was the surprise fire of Company B that caused the disastrous panic in his soldiers. Chamberlain, for his part, wrote incorrectly to his wife that his regiment had been attacked by a whole brigade.

Chamberlain seemed to have been blessed with both good timing and luck. He not only had made the right command decisions but also had managed to survive when by all rights he should have been dead. An Alabama soldier twice failed to pull the trigger of his rifle because he had second thoughts about killing the brave colonel. Then a pistol aimed and fired by a Southern officer misfired only a few feet from Chamberlain’s face.
Without the private stand of Sergeant Tozier inspiring others to close up and bolster the sagging middle of the regiment, the Confederate attacks could have eliminated the 20th Maine as a fighting force. Tozier’s bravery sparked the 20th Maine and changed the course of the engagement. Without Tozier, there would not have been an opportunity for Chamberlain to attack.
Spear, who would later become a brevet brigadier general, believed that all the officers at Little Round Top shared in the battle fully and honorably, but that the bayonet charge was a success largely due to the spirit of the enlisted men. He was convinced that only the tenacity of the 358 Maine men had enabled Chamberlain to defeat Oates’ two Alabama regiments.
Captain Howard L. Prince, former 20th Maine quartermaster-sergeant, considered Captain Morrill the coolest man in the regiment — a man who had no superior on the skirmish line. Morrill led his unit at the decisive point of the bayonet charge without orders. His contingent created the impression of two regiments rushing through the woods, though it consisted only of 44 Company B soldiers and 14 U.S. Sharpshooters. It was this group that Oates believed caused panic in his men. Without Morrill’s up-front leadership, Chamberlain’s attack probably would have been spoiled and pushed back.
Others who merited more credit than they received were Gouverneur Warren, who conducted one of the best reconnoitering jobs of the war, and Strong Vincent, who unhesitatingly put his brigade on Little Round Top and rallied that brigade under intense fire until he fell mortally wounded. Colonel Patrick O’Rorke was also one of the heroes, as his 140th New York reinforced Vincent’s brigade and saved it from early defeat. Both Vincent and O’Rorke gave their lives at Gettysburg, and if not for those two men and others, Chamberlain probably would be remembered today as only a minor figure in a major Union disaster.
Ellis Spear later suggested somewhat bitterly that the abundance of articles written by Chamberlain himself indirectly led to Chamberlain receiving sole credit for the victory. Much of the primary information about Little Round Top does come directly from Chamberlain, who published 25 separate writings on the battle. Chamberlain also was a member of the official Maine at Gettysburg Commission and wrote the organization’s chapter on the 20th Maine.
The problem with becoming a legend is that deeds may become distorted inadvertently due to commercial profits, hero worship and the sheer passage of time. Many American junior officers still look up to Chamberlain. Some take his deeds out of context, however, and mythologize him.

Chamberlain’s vivid personality overshadows the regiment that made him famous — even though it was the regiment that saved the day. There is a Chamberlain museum in Brunswick, Maine; Chamberlain Pale Ale produced in Portland, Maine; and a Chamberlain Bridge exists in Bangor, Maine — yet no commercial product commemorates the 20th Maine Volunteer Infantry. Chamberlain overshadows the 20th Maine in the way that George S. Patton overshadows the U.S. Third Army in World War II.
The valorous defense of Little Round Top will always belong to the 20th Maine Infantry and to Joshua L. Chamberlain as the regimental commander. But after weighing all the evidence, it seems fair to say that without the contributions of the 2nd Maine Infantry, Andrew J. Tozier, Company B and Holman Melcher, Chamberlain clearly and convincingly would have been defeated. Strong Vincent, Patrick O’Rorke and Ellis Spear also deserve greater recognition for their contributions. Joshua Chamberlain deserves much acclaim, but not to the exclusion of many others whom history has so far — and so unfairly — underrated.
Related Battles
23,049
28,063